
Microanalytic
Light-optical metallographic methods and/or scanning electron microscopy allow a precise analysis of the microstructure. With our partner RWTH Aachen and HDZ Aachen, we have access to these and other technically mature examination methods (e.g. confocal microscopy, EBSD, microprobe, TEM, etc.). These methods play a particularly important role in damage analysis. These methods play a particularly important role in damage analysis, to distinguish between brittle fracture, fatigue fracture and ductile fracture.
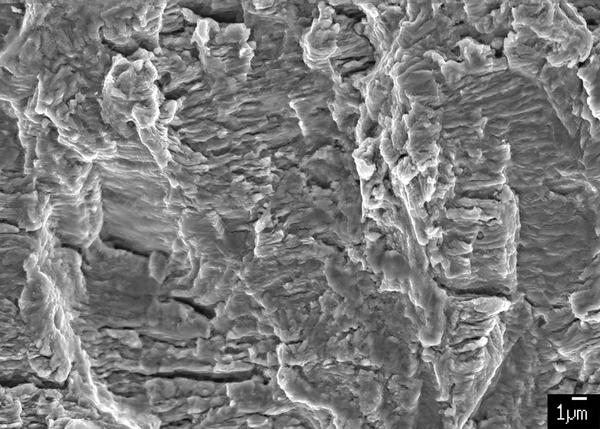
Fatigue fracture |
A fatigue fracture is a fracture that occurs under alternating load conditions. The majority of all fractures in mechanical engineering can be traced back to fatigue fractures. |
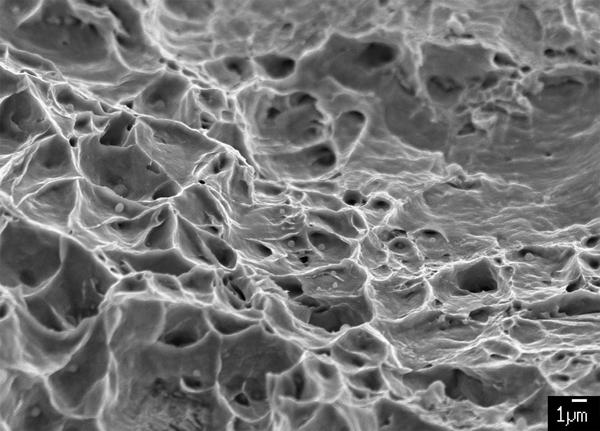
Ductile fracture |
Ductile fracture occurs in plastic deformable steels. Components or specimens deform plastically to fracture. Void formation, void growth and void fusion occur in the microstructure. |
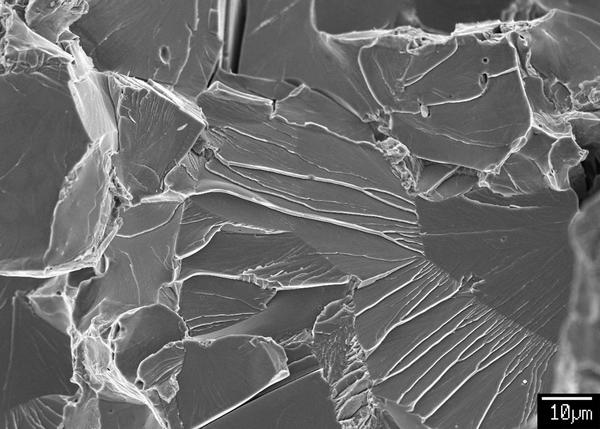
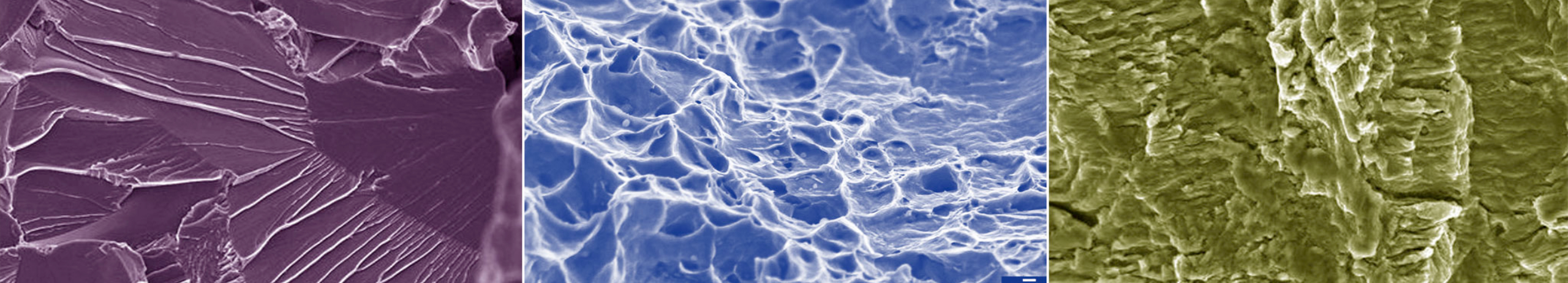
Brittle fracture |
Brittle fracture occurs in steels with transition temperature behavior at low temperatures. It is a normal stress fracture along the crystal planes (visible as facets). The cause of the cleavage fracture is the obstruction of plastic deformation on a microscopic level. |
Article on the topic of microanalytics
Round-robin test “Manual classification of microscopic fracture features”
In the course of the IGF-funded research project iFrakto, led by BAM and GFaI e.V., IWT-Solutions AG successfully participated in the round robin t
03 November, 2021Investing in digital microscopy
We are excited to present our new Keyence VHX-7000. The digitization of light microscopy creates new possibilities for material analysis and damage
15 October, 2021
Selected references on the subject of component testing
Sorry, no posts matched your criteria.


